Protects the Internal Tissues of the Body From Potential Harm
Two major forms of supportive connective tissue cartilage and bone allow the body to maintain its posture and protect internal organs. - Answers It depends on the type of aggression.

Skeletal System An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Epithelial tissue protects several aspects of your body.
. System works with the circulatory system to add oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body. A healthy immune system can defeat invading disease-causing germs or pathogens such as bacteria viruses parasitesas well as cancer cellswhile protecting healthy tissue. The integumentary system protects the bodys internal living tissues and organs protects against invasion by infectious organism and protects the body from dehydration.
They protect exposed and internal surfaces from abrasion and dehydration as well as forming a barrier against chemicals. For example your skin is made up of epithelial tissue and protects the tissues deeper in your body such as blood vessels muscle and internal organs. Determine which vessels leave enter the body.
Protects the body from physical damage. Inflammation in the liver protects this organ from infection and injury but excessive inflammation may lead to extensive loss of hepatocytes ischemia-reperfusion injury metabolic alterations and eventually permanent hepatic damage. Radiation exposure may be internal or external and can be acquired through various exposure pathways.
Understanding how the immune system. Defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism. Cells deploy an antioxidant defensive system based mainly on enzymatic components such as superoxide dismutase SOD catalase CAT and glutathione peroxidase GPx to protect themselves from ROS-induced cellular damage.
The immune system is a vast and complex interconnected network of many different organs cells and proteins that work together to protect the body from illness. Two major forms of supportive connective tissue cartilage and bone allow the body to maintain its posture and protect internal organs. Defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism endocrine system regulates the bodys metabolism growth and the functions of the sexual organs integumentary system protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm responsible for the conception of new life skeletal system.
Contracts to cause movement. Basic structural unit of the body 5. The potential damage from an absorbed dose depends on the type of radiation and the sensitivity of different tissues and organs.
Passage of substances from a body system into the circulatory system Filtration. Tissues that work together to perform a specific bodily function. The effective dose is used to measure ionizing radiation in terms of the potential for causing harm.
The cilia on the epithelial cells that line your intestines protect the rest of your body from intestinal bacteria. White blood cells that produce antibodies 3. Passage of substances through a membrane or filter.
All substances entering or leaving the body has to cross an epithelium. The distinctive appearance of cartilage is due to polysaccharides called chondroitin sulfates which bind with ground substance proteins to. They are secondarily affected.
Cytokines recruit other cells of the immune system to infected sites and stimulate their activities. Name and identify the bodys four basic tissue types and list their roles. Regulates the bodys metabolism growth and functions of the sexual organs integumentary system protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm immune system defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism reproductive system responsible for the conception of new life muscular system.
Defends your body from any organisms that threaten the destruction of cells 2. What protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm. The macrophage cells are an essential component of the immune system which is the bodys defense against potential pathogens and degraded host cells.
The distinctive appearance of cartilage is due to polysaccharides called chondroitin sulfates which bind with ground substance proteins to. Internal communication Muscle tissue. When stimulated macrophages release cytokines small proteins that act as chemical messengers.
Cells that help protect our body from radiological damage. System of vessels that are responsible for the removal of bacteria from the bloodstream 4. Primarily do not aim at tissues.
Control of permeability. An important vitamin synthesized thanks to the skin. Protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm.
Insulates body Cushions and protects internal organs. All of the above. Inflammation can destroy hepatic parenchymal cells increasing the risk of chronic liver diseases such as non-alcoholic.

4 1 Types Of Tissues Anatomy Physiology

Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology

What Is Human Body Tissue Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
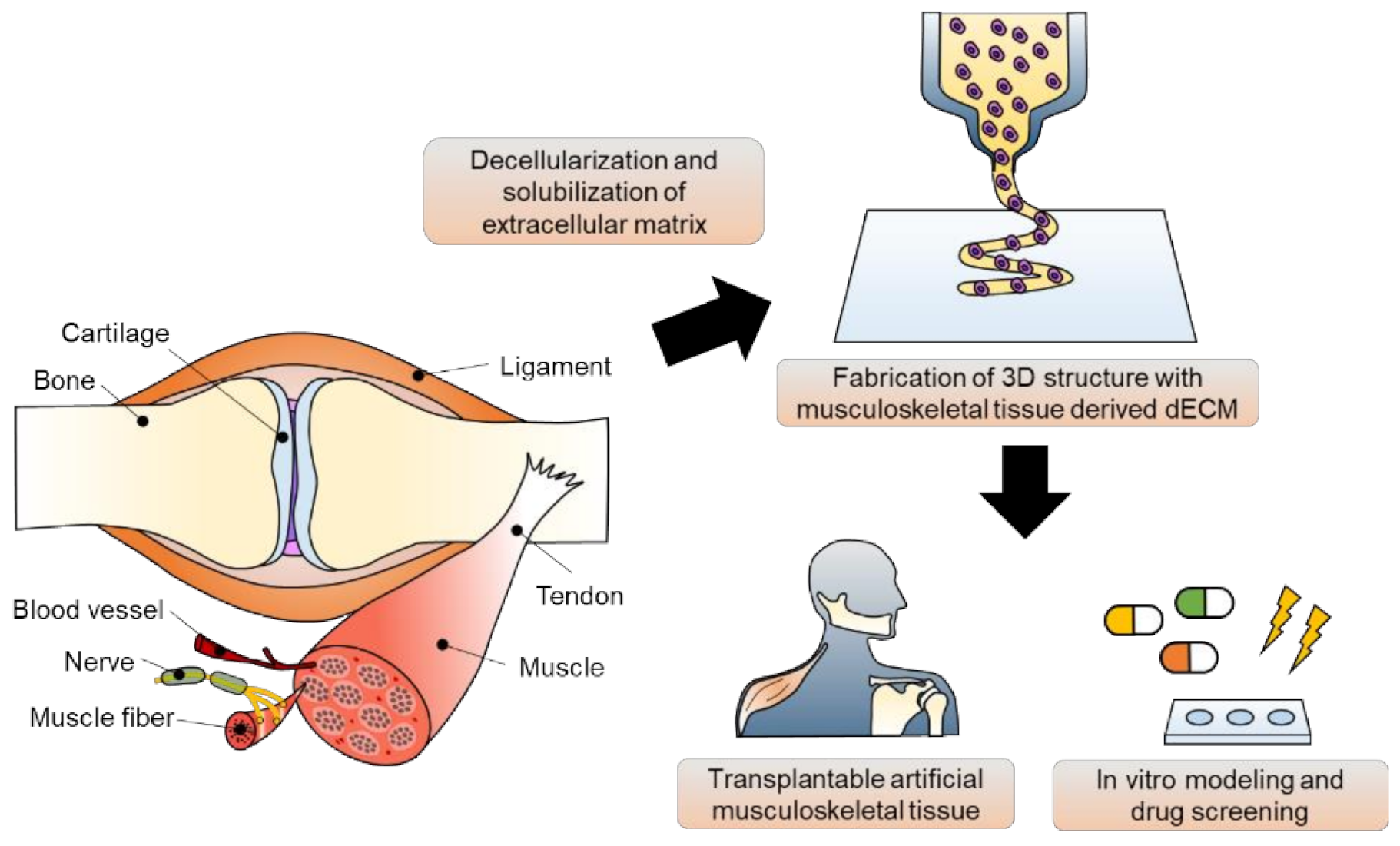
Ijms Free Full Text Tissue Specific Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Bioinks For Musculoskeletal Tissue Regeneration And Modeling Using 3d Bioprinting Technology Html

Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And Physiology I
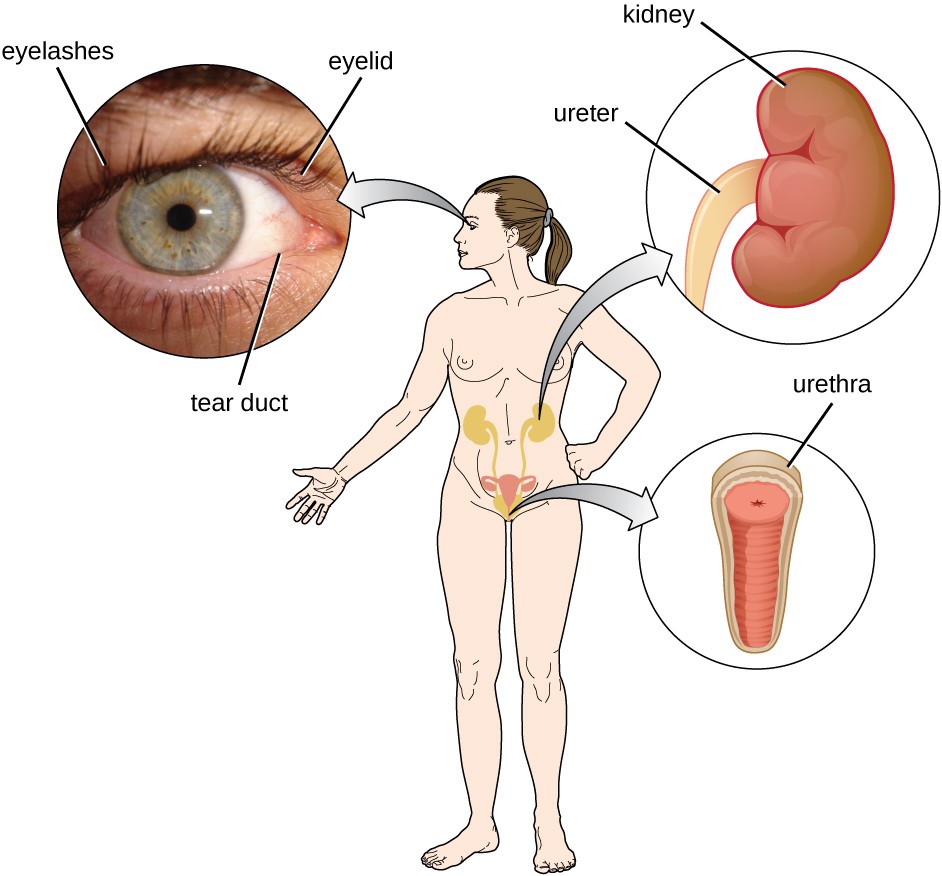
Physical Defenses Microbiology

4 1 Types Of Tissues Anatomy Physiology

Body Systems The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

5 4a Protection Medicine Libretexts

What Is Human Body Tissue Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

4 1 Types Of Tissues Anatomy Physiology
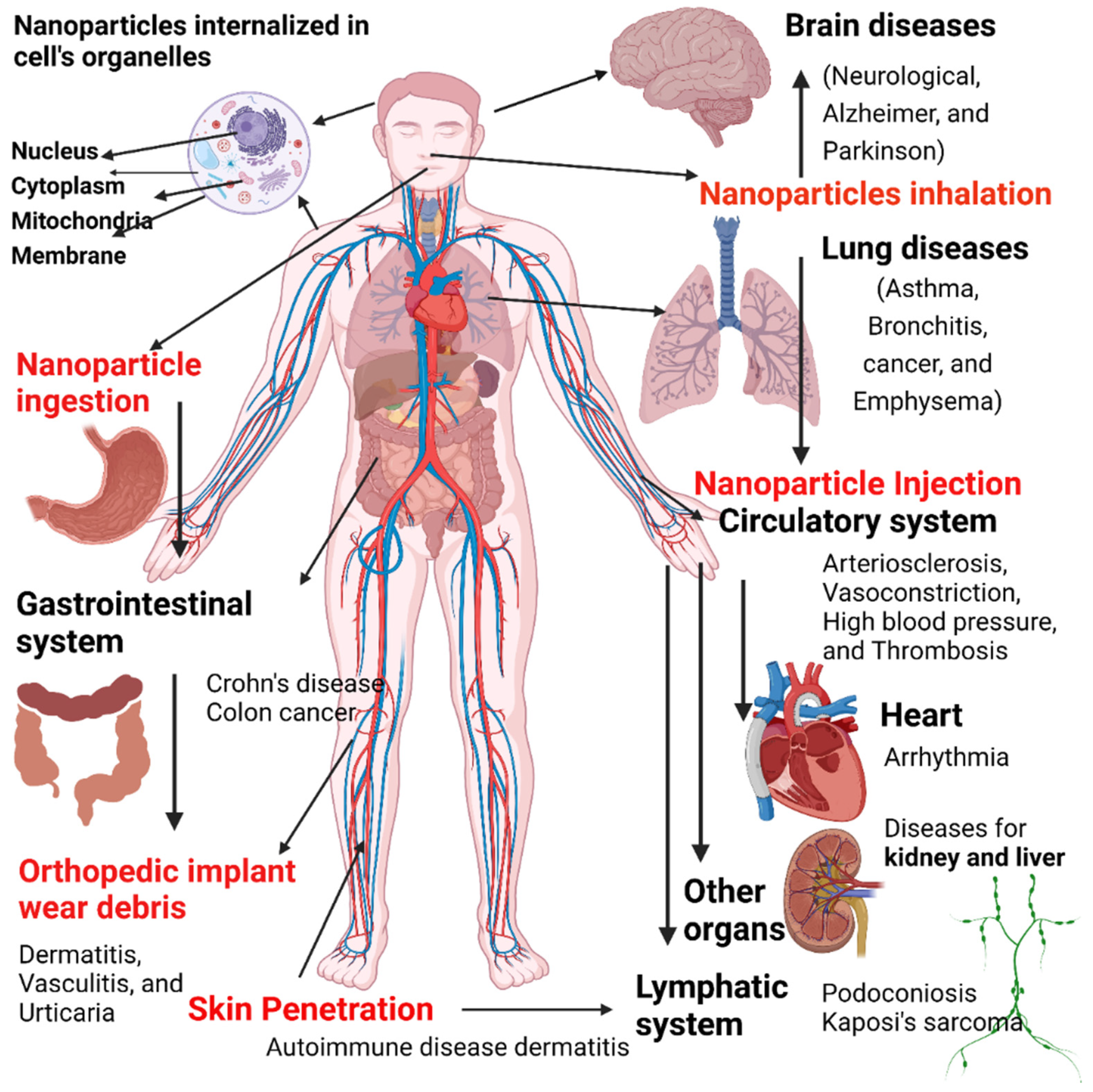
Nanomaterials Free Full Text Review On Nanoparticles And Nanostructured Materials Bioimaging Biosensing Drug Delivery Tissue Engineering Antimicrobial And Agro Food Applications Html
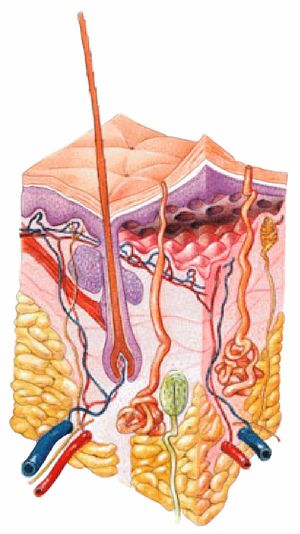
Integumentary System Physiopedia

Human Body Tissue Types Examples What Is Tissue In The Body Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
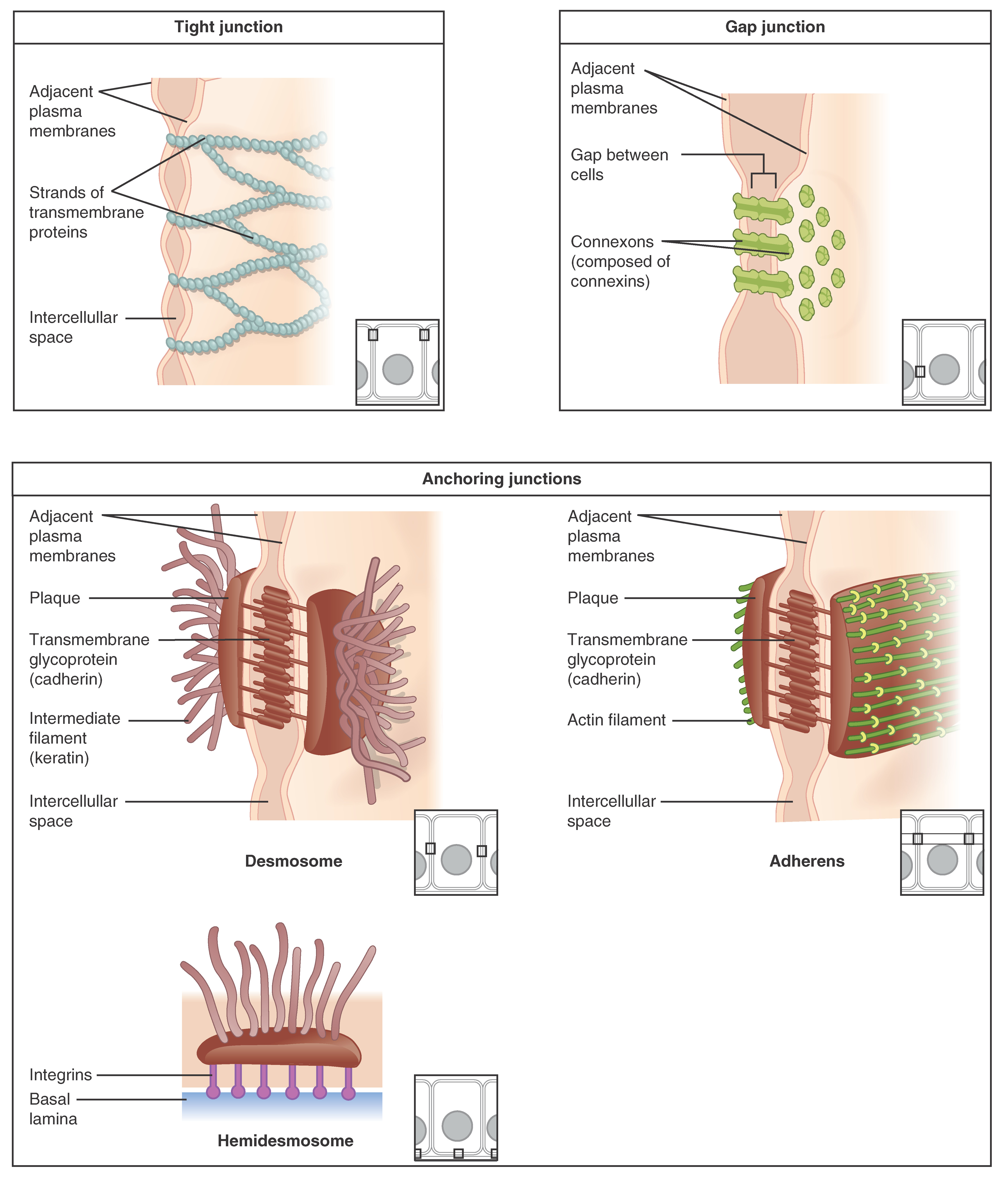
Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology

Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology